Assignment
Achievement
Hire Experts
Reviews
Free Services
Grades
Offers
Order Now
50,000+
Orders Delivered
4.9/5.0
Star Rating
100%
on-time delivery
24 x 7
Query Resolution
100 +
Subjects Catered
Our Experts
Reviews
Free Assignment Services
☞Title Pages - 100 Words
$05.00 free
☞Downloading Free Guide
$20.00 free
☞Upload Completed Tasks
$20.00 free
☞Genuine Content Report
$20.00 free
☞Consultation By Experts
$06.00 free
☞Unrestricted Revisions
$10.00 free
☞Grammar Check for Task
$25.00 free
☞Plagiarism Inspections
$25.00 free
Book Now and get Free Services Upto $0.00
Grades
Offers

1. PLACE YOUR ORDER
Whenever you fill out their order form, please read it carefully and then fill it out.

2. MAKE PAYMENT
Choose our secure payment method to pay for your order and collect your order from us with security.

3. GET YOUR DOCUMENT
Our writers write you plagiarism-free assignments and provide them to you before the deadline.
Our Experts

Search Assignments

Customers Reviews
“Climate change isn't something people get to choose to believe or not: its happening”. Despite all the claims that climate change isn’t real or the skepticism around it- The rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and discoveries of greenhouse effects have put these claims to bed. The world today is accepting its fate and showing greater urgency in addressing the issue.
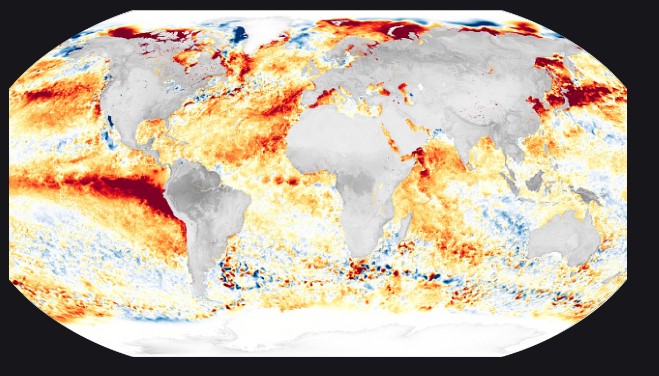
Rising global temperatures affect not only air but ocean surfaces as well. The excess heat as a result of Greenhouse effect is absorbed by the ocean surface, a number as high as- 90%. The given image shows this phenomenon with a special mention to the year 2023 which showed an extremity wrt this.
Warm colors (red, orange) show where the ocean was warmer than normal. Cool colors (blues) show where temperatures are cooler. The red swath in the Eastern Pacific was due to an El Niño event. El Niño is a climate phenomenon in the tropical Pacific that results in warmer than normal sea surface temperatures leading to weather impacts across the planet.
Increased absorption of heat and carbon dioxide by the ocean leads to increased acidification. When this happens the marine life inside the ocean like the coral reefs are unable to grow and protect themselves. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as coral bleaching. (as indicated in the image).

The mountain and glacier ecosystem is particularly vulnerable to climate change, as the effects of increased temperatures are clearly evident in these parts.
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world- whether Himalayas, Andes, Alps or Alaska.

Columbia Glacier, Alaska, has retreated by 6.5 km (4 miles) between 2009 (left) and 2015 (right)- newatlas.com
Increase in overall carbon emission, and greenhouse gas effect has inflated the global temperatures by 1 degree Celsius since the 19th century with most of the increase in the past 40 years. 2016 and 2020 tied on top for being the warmest on record.
So whether we acknowledge it or not, it’s a fact that climate change is serious, and continues to reshape our planet for which urgent action is required.

The history of climate change being recognized as a global problem dates back to 1979. The first world climate conference held in Geneva 1979 sponsored by the WMO World Meteorological Organization thoroughly discussed the issue for the first time.
This led to a series of discussions and meetings to seek solutions for the issue. It was finally in 1992 at the First RIO UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) that the concept of reducing Greenhouse Gas emissions was taken up.

The UNFCCC led to the adoption of various other key frameworks like-
|
1997 Kyoto Protocol |
Binding emission targets |
|
2015 Paris Agreement / COP21 |
Aims to limit global warming to a target below 2 degrees Celsius preferably - 1.5 degrees Celsius. |
The Paris Agreement (2015) remains the cornerstone of global climate action, aiming to limit global warming to 1.5°C or 2°C above pre-industrial levels. Countries regularly update their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to reduce emissions.
Steps are being taken by the countries to invest in renewable sources of energy like Solar, Wind, Hydropower, and Nuclear. The technological advancements and innovations with respect to employing EVs (Electric Vehicles) and CCS-Carbon Capture and Storage are also being taken.
Climate Finance:
Wealthier nations have committed billions to assist developing countries in adapting to climate change effects and transitioning to low-carbon economies.
Reforestation and Nature-Based Solutions:
Programs like the Trillion Tree Campaign stress reforestation and forest conservation to increase carbon sinks. Mangroves and wetlands are being used by coastal restoration projects to deal with sea-level rise and biodiversity.

Climate change is a very volatile issue that needs regular assessment and monitoring of the roadmap set to tackle it. COP 28 held in Dubai UAE from November 30 to December 12, 2023 reaffirms the need for global collaboration to solve the problem. The main emphasis highlighted the need to come together, whether it’s businesses, governments, or individuals.
Below is a detailed account of the key discussions and initiatives emphasized during COP28:
Regenerative Agriculture and Sustainable Food Systems
During the COP 28 discussions a significant focus was placed on Regenerative agriculture, gardens and farms in providing sustainability to the agriculture sector. Thereby building resilience against climate change.
Protecting Nature for Climate, Lives, and Livelihoods
Protecting natural ecosystems was at the heart of the discussions, recognizing the interconnectedness between climate resilience and biodiversity conservation. The need for immediate action was emphasized by concerning trends: global temperatures approaching the crucial 1.5°C limit and humanity's decreasing ability to adapt.
Nature-Based Solutions (NBS): The importance of relying on nature was stressed as vital for mitigating the worsening effects of climate change. Forests, wetlands, and coastal ecosystems serve as protective barriers against severe weather, making their conservation essential for sustaining climate stability.
Safeguarding our Oceans and Seas
The oceans play a key role in absorbing carbon and controlling global temperatures making them a main topic at COP28. The event aimed to bring scientists together to agree on ocean-related issues such as:
Ratification of the UN Agreement on High Seas: The summit saw important steps in controlling the use of waters outside national borders to protect marine life.
Illegal Fishing and Marine Pollution: Talks focused on creating worldwide agreements to fight illegal fishing and push for binding rules on plastics that end up in the ocean.
Seabed Protection: People at the summit saw protecting the seabed, which is full of diverse life, as key to keeping the oceans healthy.
Safeguarding Fragile Mountain Environments
Mountains, which 15% of people worldwide call home, are seen as key ecosystems that climate change hits hard. They act as big natural water stores and play their part in keeping food supplies steady helping to keep nature in balance. The talks stressed the need to cut down on harm to the mountain environment using targeted plans.
Climate Change, Biodiversity, and Equity
COP28 aimed to formulate new strategies aimed for Climate change and Biodiversity conservation simultaneously which would require equal participation of all the stakeholders from developing countries to marginalized communities.
Scaling up Renewable energy in the form of Nuclear power
Signing up of an agreement where 16 countries aimed to triple global nuclear by 2050 also took place in COP28. A step important towards a new future of renewable energy. COP28 was special because there was a first time mention of official transitioning from fossil fuels as well.
While COP28 made important commitments to climate action, there are still doubts about whether these initiatives are enough to tackle the growing crisis. Progress has been seen in areas like renewable energy, ecosystem protection, and promoting equity, but the speed of implementation remains inadequate. The Global Stocktake indicated that current efforts are falling short of the goal to limit warming to 1.5°C.
Critical areas that require immediate focus include enforceable commitments to phase out fossil fuels, a significant increase in climate finance, and ensuring that promised funds are actually delivered. Vulnerable nations, which are often the least responsible for emissions, need urgent assistance to adapt to climate impacts and recover from losses.
Additionally, advancements in carbon capture technology, the development of circular economies to minimize waste, and stronger accountability measures for achieving targets are essential. Governments need to implement stricter regulations on emissions, businesses should commit to transparent sustainability practices, and individuals must adopt low-carbon lifestyles.
The most urgent requirement is global solidarity—cooperation between developed and developing countries to share technology, knowledge, and resources. COP28 represents progress, but to effectively address climate change, the world must act with increased urgency and unity. Only then can we aspire to secure a sustainable future for everyone.
Disclaimer: all content and intellectual property remain the exclusive property of value Assignment Help




No Comments